Kamis, 18 November 2010
Castor Bean
5. Castor Bean
Tanaman castor bean atau dikenal dengan Ricinus communis secara luas dibudidayakan untuk castor oil dan juga sebagai tanaman hias. Pada kenyataannya tanaman ini mengandung racun mematikan yang disebut dengan ricin. Dulunya tanaman ini banyak ditemukan di Afrika, tapi sekarang bisa ditemukan di seluruh dunia. Tanaman ini tumbuh dengan baik di daerah tandus dan tidak memerlukan perawatan khusus.
Sebagian besar ricin terkonsentrasi di lapisan benih, karenanya mengonsumsi 3 benih tanaman ini sudah bisa mematikan seorang anak. Gejala keracunan benih ini adalah mual, kram perut, muntah, pendarahan internal, kegagalan sirkulasi dan ginjal. Selain itu debu yang menempel di benih ini juga bisa menimbulkan reaksi alergi seperti batuk, nyeri otot dan kesulitan bernapas.
Deadly Nightshade
4. Deadly Nightshade
Deadly nightshade atau Atropa belladonna mengandung racun atropine dan scopolamine di dalam batang, daun, buah dan akar. Tanaman ini tumbuh setinggi 0,6-1,2 meter dengan daun hijau gelap dan berbentuk lonceng ungu. Bunganya akan mekar di pertengahan musim panas. Hanya ditemui pada beberapa wilayah di dunia.
Racun yang ada bisa mempengaruhi sistem saraf. Pada dosis yang cukup, racun akan melumpuhkan ujung saraf dari otot seperti pembuluh darah, jantung dan otot gastrointestinal. Gejala keracunan yang timbul adalah pupil membesar atau melebar, lebih peka terhadap cahaya, penglihatan kabur, sakit kepala, kebingungan dan kejang. Menelan 2 buah ini bisa membunuh seorang anak, jika 10-20 buah bisa membunuh seorang dewasa.
Deadly nightshade atau Atropa belladonna mengandung racun atropine dan scopolamine di dalam batang, daun, buah dan akar. Tanaman ini tumbuh setinggi 0,6-1,2 meter dengan daun hijau gelap dan berbentuk lonceng ungu. Bunganya akan mekar di pertengahan musim panas. Hanya ditemui pada beberapa wilayah di dunia.
Racun yang ada bisa mempengaruhi sistem saraf. Pada dosis yang cukup, racun akan melumpuhkan ujung saraf dari otot seperti pembuluh darah, jantung dan otot gastrointestinal. Gejala keracunan yang timbul adalah pupil membesar atau melebar, lebih peka terhadap cahaya, penglihatan kabur, sakit kepala, kebingungan dan kejang. Menelan 2 buah ini bisa membunuh seorang anak, jika 10-20 buah bisa membunuh seorang dewasa.
Rosary Pea
3. Rosary Pea
Tanaman rosary pea atau Abrus precatorius adalah benih yang cantik dilihat dengan perpaduan warna merah dan hitam, sehingga sering digunakan untuk perhiasan. Benih ini mengandung racun abrin dan akan berbahaya jika lapisan benih rusak atau tergores. Karenanya pembuat perhiasan lebih rentan terkena racun dibanding pemakainya. Tanaman ini bisa mencapai tinggi 20 meter dan menyebar di seluruh negara terutama negara beriklim tropis dan sub-tropis.
Racun abrin ini lebih mematikan dibanding ricin, karena kurang dari 3 mikrogram abrin atau tidak sampai satu benih sudah cukup mematikan. Gejala keracunan yang muncul adalah sulit bernapas, demam, mual, ada cairan di paru-paru. Jika benih tersebut tertelan bisa menyebabkan mual, muntah, dehidrasi, gagal ginjal, hati dan limpa. Kematian biasanya terjadi dalam waktu 3-5 hari.
Tanaman rosary pea atau Abrus precatorius adalah benih yang cantik dilihat dengan perpaduan warna merah dan hitam, sehingga sering digunakan untuk perhiasan. Benih ini mengandung racun abrin dan akan berbahaya jika lapisan benih rusak atau tergores. Karenanya pembuat perhiasan lebih rentan terkena racun dibanding pemakainya. Tanaman ini bisa mencapai tinggi 20 meter dan menyebar di seluruh negara terutama negara beriklim tropis dan sub-tropis.
Racun abrin ini lebih mematikan dibanding ricin, karena kurang dari 3 mikrogram abrin atau tidak sampai satu benih sudah cukup mematikan. Gejala keracunan yang muncul adalah sulit bernapas, demam, mual, ada cairan di paru-paru. Jika benih tersebut tertelan bisa menyebabkan mual, muntah, dehidrasi, gagal ginjal, hati dan limpa. Kematian biasanya terjadi dalam waktu 3-5 hari.
water hemlock
2. Water Hemlock
Tanaman water hemlock atau Cicuta maculata adalah tanaman yang menarik dengan daun ungu bergaris-garis putih serta berbuah kecil. Tanaman ini berasal dari Amerika Utara dengan tinggi mencapai 1,8 meter serta tumbuh subur di sepanjang tepi sungai, rawa, dataran rendah dan padang rumput yang basah.
Racun yang terkandung dalam tanaman ini disebut dengan cicutoxin yang ada diseluruh tanaman dan paling terkonsentrasi di akar. Racun ini menyebabkan kejang yang kaku dan menyakitkan, mual, muntah, kram dan tremor (gemetar) otot. Kalaupun selamat dari racun ini biasanya akan menderita amnesia.
Tanaman water hemlock atau Cicuta maculata adalah tanaman yang menarik dengan daun ungu bergaris-garis putih serta berbuah kecil. Tanaman ini berasal dari Amerika Utara dengan tinggi mencapai 1,8 meter serta tumbuh subur di sepanjang tepi sungai, rawa, dataran rendah dan padang rumput yang basah.
5 Tanaman paling beracun di dunia
Oleander
Tanaman oleander atau Nerium oleander dianggap sebagai tanaman paling beracun di dunia. Karena seluruh bagian tanaman mengandung racun dan terdiri dari beberapa jenis racun. Tapi racun yang paling berbahaya adalah oleandrin dan neriine yang bisa berefek kuat pada jantung.
Meski demikian tanaman ini sering digunakan sebagai dekorasi dan berasal dari daerah mediterania dengan tinggi mencapai 1,8-5,4 meter.
Jka menelan daun yang mengandung racun ini akan menimbulkan gejala diare, muntah, sakit perut hebat, mengantuk, pusing, denyut jantung tidak teratur serta kematian. Jika korban ditolong sebelum 24 jam, maka peluang untuk selamatnya tinggi. Biasanya pasien didorong untuk muntah dengan memompa perutnya atau mengonsumsi arang aktif untuk menyerap racun.
Tanaman oleander atau Nerium oleander dianggap sebagai tanaman paling beracun di dunia. Karena seluruh bagian tanaman mengandung racun dan terdiri dari beberapa jenis racun. Tapi racun yang paling berbahaya adalah oleandrin dan neriine yang bisa berefek kuat pada jantung.
Meski demikian tanaman ini sering digunakan sebagai dekorasi dan berasal dari daerah mediterania dengan tinggi mencapai 1,8-5,4 meter.
Jka menelan daun yang mengandung racun ini akan menimbulkan gejala diare, muntah, sakit perut hebat, mengantuk, pusing, denyut jantung tidak teratur serta kematian. Jika korban ditolong sebelum 24 jam, maka peluang untuk selamatnya tinggi. Biasanya pasien didorong untuk muntah dengan memompa perutnya atau mengonsumsi arang aktif untuk menyerap racun.
Kuta Bali
History
Main article: History of Bali
Bali was inhabited by about 2000 BC by Austronesian peoples who migrated originally from Taiwan through Maritime Southeast Asia.[3] Culturally and linguistically, the Balinese are thus closely related to the peoples of the Indonesian archipelago, the Philippines, and Oceania.[4] Stone tools dating from this time have been found near the village of Cekik in the island's west.[5]Balinese culture was strongly influenced by Indian and Chinese, and particularly Hindu culture, in a process beginning around the 1st century AD. The name Bali dwipa ("Bali island") has been discovered from various inscriptions, including the Blanjong pillar inscription written by Sri Kesari Warmadewa in 914 AD and mentioning "Walidwipa". It was during this time that the complex irrigation system subak was developed to grow rice. Some religious and cultural traditions still in existence today can be traced back to this period. The Hindu Majapahit Empire (1293–1520 AD) on eastern Java founded a Balinese colony in 1343. When the empire declined, there was an exodus of intellectuals, artists, priests and musicians from Java to Bali in the 15th century.
The first European contact with Bali is thought to have been made in 1585 when a Portuguese ship foundered off the Bukit Peninsula and left a few Portuguese in the service of Dewa Agung[6]. In 1597 the Dutch explorer Cornelis de Houtman arrived at Bali and, with the establishment of the Dutch East India Company in 1602, the stage was set for colonial control two and a half centuries later when Dutch control expanded across the Indonesian archipelago throughout the second half of the nineteenth century (see Dutch East Indies). Dutch political and economic control over Bali began in the 1840s on the island's north coast, when the Dutch pitted various distrustful Balinese realms against each other.[7] In the late 1890s, struggles between Balinese kingdoms in the island's south were exploited by the Dutch to increase their control.
The Dutch mounted large naval and ground assaults at the Sanur region in 1906 and were met by the thousands of members of the royal family and their followers who fought against the superior Dutch force in a suicidal puputan defensive assault rather than face the humiliation of surrender.[7] Despite Dutch demands for surrender, an estimated 1,000 Balinese marched to their death against the invaders.[8] In the Dutch intervention in Bali (1908), a similar massacre occurred in the face of a Dutch assault in Klungkung. Afterwards the Dutch governors were able to exercise administrative control over the island, but local control over religion and culture generally remained intact. Dutch rule over Bali came later and was never as well established as in other parts of Indonesia such as Java and Maluku.
In the 1930s, anthropologists Margaret Mead and Gregory Bateson, and artists Miguel Covarrubias and Walter Spies, and musicologist Colin McPhee created a western image of Bali as "an enchanted land of aesthetes at peace with themselves and nature", and western tourism first developed on the island.[9]

Balinese dancers show for tourists, Ubud.
The 1963 eruption of Mount Agung killed thousands, created economic havoc and forced many displaced Balinese to be transmigrated to other parts of Indonesia. Mirroring the widening of social divisions across Indonesia in the 1950s and early 1960s, Bali saw conflict between supporters of the traditional caste system, and those rejecting these traditional values. Politically, this was represented by opposing supporters of the Indonesian Communist Party (PKI) and the Indonesian Nationalist Party (PNI), with tensions and ill-feeling further increased by the PKI's land reform programs.[7] An attempted coup in Jakarta was put down by forces led by General Suharto. The army became the dominant power as it instigated a violent anti-communist purge, in which the army blamed the PKI for the coup. Most estimates suggest that at least 500,000 people were killed across Indonesia, with an estimated 80,000 killed in Bali, equivalent to 5% of the island's population.[11] With no Islamic forces involved as in Java and Sumatra, upper-caste PNI landlords led the extermination of PKI members.[12]
As a result of the 1965/66 upheavals, Suharto was able to manoeuvre Sukarno out of the presidency, and his "New Order" government reestablished relations with western countries. The pre-War Bali as "paradise" was revived in a modern form, and the resulting large growth in tourism has led to a dramatic increase in Balinese standards of living and significant foreign exchange earned for the country.[7] A bombing in 2002 by militant Islamists in the tourist area of Kuta killed 202 people, mostly foreigners. This attack, and another in 2005, severely affected tourism, bringing much economic hardship to the island. Tourist numbers have now returned to levels before the bombings.
[edit] Geography
See also: List of bodies of water in Bali and List of mountains in Bali
The island of Bali lies 3.2 km (2 mi) east of Java, and is approximately 8 degrees south of the equator. Bali and Java are separated by Bali Strait. East to west, the island is approximately 153 km (95 mi) wide and spans approximately 112 km (69 mi) north to south; its land area is 5,632 km².Bali's central mountains include several peaks over 2,000 metres. The highest is Mount Agung (3,142 m), known as the "mother mountain" which is an active volcano. Mountains range from centre to the eastern side, with Mount Agung the easternmost peak. Bali's volcanic nature has contributed to its exceptional fertility and its tall mountain ranges provide the high rainfall that supports the highly productive agriculture sector. South of the mountains is a broad steadily descending area where most of Bali's large rice crop is grown. The northern side of the mountains slopes more steeply to the sea and is the main coffee producing area of the island, along with rice, vegetables and cattle. The longest river, Ayung River, flows approximately 75 km.
The island is surrounded by coral reefs. Beaches in the south tend to have white sand while those in the north and west have black sand. Bali has no major waterways, although the Ho River is navigable by small sampan boats. Black sand beaches between Pasut and Klatingdukuh are being developed for tourism, but apart from the seaside temple of Tanah Lot, they are not yet used for significant tourism.
The largest city is the provincial capital, Denpasar, near the southern coast. Its population is around 491,500(2002). Bali's second-largest city is the old colonial capital, Singaraja, which is located on the north coast and is home to around 100,000 people. Other important cities include the beach resort, Kuta, which is practically part of Denpasar's urban area; and Ubud, which is north of Denpasar, and is known as the island's cultural centre.
Three small islands lie to the immediate south east and all are administratively part of the Klungkung regency of Bali: Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan and Nusa Ceningan. These islands are separated from Bali by the Badung Strait.
To the east, the Lombok Strait separates Bali from Lombok and marks the biogeographical division between the fauna of the Indomalayan ecozone and the distinctly different fauna of Australasia. The transition is known as the Wallace Line, named after Alfred Russel Wallace, who first proposed a transition zone between these two major biomes. When sea levels dropped during the Pleistocene ice age, Bali was connected to Java and Sumatra and to the mainland of Asia and shared the Asian fauna, but the deep water of the Lombok Strait continued to keep Lombok and the Lesser Sunda archipelago isolated.
[edit] Ecology

The Bali Starling is found only on Bali and is critically endangered.
Until the early 20th century, Bali was home to several large mammals: the wild Banteng, Leopard and an endemic subspecies of Tiger, the Bali Tiger. The Banteng still occurs in its domestic form, while leopards are found only in neighboring Java, and the Bali Tiger is extinct. The last definite record of a Tiger on Bali dates from 1937, when one was shot, though the subspecies may have survived until the 1940s or 1950s.[13] The relatively small size of the island, conflict with humans, poaching and habitat reduction drove the Tiger to extinction. This was the smallest and rarest of all Tiger subspecies and was never caught on film or displayed in zoos, while few skins or bones remain in museums around the world. Today, the largest mammals are the Javan Rusa deer and the Wild Boar. A second, smaller species of deer, the Indian Muntjac, also occurs.

Monkey Forest, Ubud.
Snakes include the King Cobra and Reticulated Python. The Water Monitor can grow to an impressive size and move surprisingly quickly.
The rich coral reefs around the coast, particularly around popular diving spots such as Tulamben, Amed, Menjangan or neighboring Nusa Penida, host a wide range of marine life, for instance Hawksbill Turtle, Giant Sunfish, Giant Manta Ray, Giant Moray Eel, Bumphead Parrotfish, Hammerhead Shark, Reef Shark, barracuda, and sea snakes. Dolphins are commonly encountered on the north coast near Singaraja and Lovina.
Many plants have been introduced by humans within the last centuries, particularly since the 20th century, making it sometimes hard to distinguish what plants are really native. Among the larger trees the most common are: Banyan trees, Jackfruit, coconuts, bamboo species, acacia trees and also endless rows of coconuts and banana species. Numerous flowers can be seen: hibiscus, frangipani, bougainvillea, poinsettia, oleander, jasmine, water lily, lotus, roses, begonias, orchids and hydrangeas exist. On higher grounds that receive more moisture, for instance around Kintamani, certain species of fern trees, mushrooms and even pine trees thrive well. Rice comes in many varieties. Other plants with agricultural value include: salak, mangosteen, corn, Kintamani orange, coffee and water spinach.
[edit] Administrative divisions
The province is divided into 8 regencies (kabupaten) and 1 city (kota). Unless otherwise stated, the regency's capital:- Badung, capital Mangupura
- Bangli, capital Bangli
- Buleleng, capital Singaraja
- Denpasar (city)
- Gianyar, capital Gianyar
- Jembrana, capital Negara
- Karangasem, capital Amlapura
- Klungkung, capital Semarapura
- Tabanan, capital Tabanan
[edit] Economy
Three decades ago, the Balinese economy was largely agriculture-based in terms of both output and employment. Tourism is now the largest single industry; and as a result, Bali is one of Indonesia’s wealthiest regions. About 80% of Bali's economy depends on tourism.[14] The economy, however, suffered significantly as a result of the terrorist bombings 2002 and 2005. The tourism industry is slowly recovering once again.[edit] Agriculture
Although tourism produces the GDP’s largest output, agriculture is still the island’s biggest employer;[15][citation needed] most notably rice cultivation. Crops grown in smaller amounts include fruit, vegetables, Coffea arabica and other cash and subsistence crops.[citation needed] Fishing also provides a significant number of jobs. Bali is also famous for its artisans who produce a vast array of handicrafts, including batik and ikat cloth and clothing, wooden carvings, stone carvings, painted art and silverware. Notably, individual villages typically adopt a single product, such as wind chimes or wooden furniture.The Arabica coffee production region is the highland region of Kintamani near Mount Batur. Generally, Balinese coffee is processed using the wet method. This results in a sweet, soft coffee with good consistency. Typical flavors include lemon and other citrus notes.[16] Many coffee farmers in Kintamani are members of a traditional farming system called Subak Abian, which is based on the Hindu philosophy of "Tri Hita Karana”. According to this philosophy, the three causes of happiness are good relations with God, other people and the environment. The Subak Abian system is ideally suited to the production of fair trade and organic coffee production. Arabica coffee from Kintamani is the first product in Indonesia to request a Geographical Indication.[17]
[edit] Tourism
The tourism industry is overwhelmingly focused in the south, while significant in the other parts of the island as well. The main tourist locations are the town of Kuta (with its beach), and its outer suburbs (which were once independent townships) of Legian and Seminyak; the east coast town of Sanur (once the only tourist hub); in the center of the island Ubud; to the south of the airport is Jimbaran and the newer development of Nusa Dua.Another increasingly important source of income for Bali is what is called "Congress Tourism" from the frequent international conferences held on the island. The number of these events increased after the terrorist bombings of 2002 and 2005, to resurrect Bali's damaged tourism industry as well as its tarnished image. One such event was the 2010 World Geothermal Congress.
The American government lifted its travel warnings in 2008. As of 2009 the Australian government still rates it a 4 danger level (the same as several countries in central Africa) on a scale of 5.
An offshoot of tourism is the growing real estate industry. Bali real estate has been rapidly developing in the main tourist areas of Kuta, Legian, Seminyak and Oberoi. Most recently, high-end 5 star projects are under development on the Bukit peninsula on the south side of the island. Million dollar villas are springing up along the cliff sides of south Bali, commanding panoramic ocean views. Foreign and domestic (many Jakarta individuals and companies are fairly active) investment into other areas of the island also continues to grow. Land prices, despite the worldwide economic crisis have remained stable.
In the last half of 2008, Indonesia's currency had dropped approximately 30% against the US dollar, providing many overseas visitors value for their currencies. Visitor arrivals for 2009 were forecast to drop 8% (which would be higher than 2007 levels), due to the worldwide economic crisis which has also affected the global tourist industry and not due to any travel warnings.
Bali's tourism economy has not only survived the terrorist bombings of 2002 and 2005, the tourism industry has slowly recovered and surpassed its pre-terrorist bombing levels and the longterm trend is a steady increase of visitor arrivals.
One of Bali's main tourist incomes is from the Scuba Diving Industry. It is an industry that has thrived over the past decade or so with the influx of new tourism and the great array of dive sites available. The seasonal Mola Mola (oceanic Sunfish) bring in large numbers of guests during the months of July - October, with Nusa Penida being the most frequented dive location. Bali diving is also on up in the Professional Development market where training happens for recreational divers who want try a new challenge can step up to the level of PADI Divemaster and Instructor. In fact recently one particular dive outfit in Sanur Bali has offered to the world a chance to train in Bali completely free for 7 months up to PADI Instructor level.
The Indonesian Tourism Ministry expects more visitors arrivals in 2010, whose target for visitor arrivals is aimed to be the highest ever.[18]
Bali's tourism brand is Bali Shanti Shanti Shanti.[19] Where Shanti derived from Sanskrit "Shanti" (शान्ति) meaning peace.
Bali, received the Best Island award from Travel and Leisure 2010. The award was presented in the show "World's Best Awards 2010" in New York, on 21 July. Hotel Four Seasons Resort Bali at Jimbaran also received an award in the category of "World Best Hotel Spas in Asia 2010". The award was based upon survey results of travel magazine Travel + Leisure readers, during the period December 15, 2009 through March 31, 2010, and was based upon several criteria. The island of Bali won because its natural state is uniformly attractive (both mountain and coastal areas), tourist attractions are diverse and widely distributed, the excellent availability of restaurants food (international and local), and the friendliness of the local people to visitors.
[edit] Transportation
The Ngurah Rai International Airport is located near Jimbaran, on the isthmus at the southernmost part of the island. Lt.Col. Wisnu Airfield is found in north-west Bali.A coastal road surrounds the island, and three major two-lane arteries cross the central mountains at passes reaching to 1,750m in height (at Penelokan). The Ngurah Rai Bypass is a four-lane expressway that partly encircles Denpasar and enables cars to travel quickly in the heavily populated south. Bali has no railway lines.
[edit] Demographics
The population of Bali is 3,151,000 (as of 2005). There are an estimated 30,000 expatriates living in Bali.[20][edit] Religion
Unlike most of Muslim-majority Indonesia, about 93.18% of Bali's population adheres to Balinese Hinduism, formed as a combination of existing local beliefs and Hindu influences from mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. Minority religions include Islam (4.79%), Christianity (1.38%), and Buddhism (0.64%). These figures do not include immigrants from other parts of Indonesia.When Islam surpassed Hinduism in Java (16th century), Bali became a refuge for many Hindus. Balinese Hinduism is an amalgam in which gods and demigods are worshipped together with Buddhist heroes, the spirits of ancestors, indigenous agricultural deities and sacred places. Religion as it is practiced in Bali is a composite belief system that embraces not only theology, philosophy, and mythology, but ancestor worship, animism and magic. It pervades nearly every aspect of traditional life. Caste is observed, though less strictly than in India. With an estimated 20,000 puras (temples) and shrines, Bali is known as the "Island of a Thousand Puras", or "Island of the Gods".[21]
Balinese Hinduism has roots in Indian Hinduism and in Buddhism, and adopted the animistic traditions of the indigenous people. This influence strengthened the belief that the gods and goddesses are present in all things. Every element of nature, therefore, possesses its own power, which reflects the power of the gods. A rock, tree, dagger, or woven cloth is a potential home for spirits whose energy can be directed for good or evil. Balinese Hinduism is deeply interwoven with art and ritual. Ritualizing states of self-control are a notable feature of religious expression among the people, who for this reason have become famous for their graceful and decorous behavior.[22]
Apart from the majority of Balinese Hindus, there also exist Chinese immigrants whose traditions have melded with that of the locals. As a result, these Sino-Balinese not only embrace their original religion, which is a mixture of Buddhism, Taoism and Confucianism, but also find a way to harmonise it with the local traditions. Hence, it is not uncommon to find local Sino-Balinese during the local temple's odalan. Moreover, Balinese Hindu priests are invited to perform rites alongside a Chinese priest in the event of the death of a Sino-Balinese.[23] Nevertheless, the Sino-Balinese claim to embrace Buddhism for administrative purposes, such as their Identity Cards.[24]
[edit] Language
Balinese and Indonesian are the most widely spoken languages in Bali, and the vast majority of Balinese people are bilingual or trilingual. There are several indigenous Balinese languages, but most Balinese can also use the most widely spoken option: modern common Balinese. The usage of different Balinese languages was traditionally determined by the Balinese caste system and by clan membership, but this tradition is diminishing.English is a common third language (and the primary foreign language) of many Balinese, owing to the requirements of the tourism industry.
[edit] Culture
Main articles: Music of Bali and Balinese art
Bali is renowned for its diverse and sophisticated art forms, such as painting, sculpture, woodcarving, handcrafts, and performing arts. Balinese percussion orchestra music, known as gamelan, is highly developed and varied. Balinese performing arts often portray stories from Hindu epics such as the Ramayana but with heavy Balinese influence. Famous Balinese dances include pendet, legong, baris, topeng, barong, gong keybar, and kecak (the monkey dance). Bali boasts one of the most diverse and innovative performing arts cultures in the world, with paid performances at thousands of temple festivals, private ceremonies, or public shows.[25]The Hindu New Year, Nyepi, is celebrated in the spring by a day of silence. On this day everyone stays at home and tourists are encouraged to remain in their hotels. But the day before that large, colourful sculptures of ogoh-ogoh monsters are paraded and finally burned in the evening to drive away evil spirits. Other festivals throughout the year are specified by the Balinese pawukon calendrical system.
Celebrations are held for many occasions such as a tooth-filing (coming-of-age ritual), cremation or odalan (temple festival). One of the most important concepts that Balinese ceremonies have in common is that of désa kala patra, which refers to how ritual performances must be appropriate in both the specific and general social context.[26] Many of the ceremonial art forms such as wayang kulit and topeng are highly improvisatory, providing flexibility for the performer to adapt the performance to the current situation.[27] Many celebrations call for a loud, boisterous atmosphere with lots of activity and the resulting aesthetic, ramé, is distinctively Balinese. Oftentimes two or more gamelan ensembles will be performing well within earshot, and sometimes compete with each other in order to be heard. Likewise, the audience members talk amongst themselves, get up and walk around, or even cheer on the performance, which adds to the many layers of activity and the liveliness typical of ramé.[28]
Kaja and kelod are the Balinese equivalents of North and South, which refer to ones orientation between the island’s largest mountain Gunung Agung (kaja), and the sea (kelod). In addition to spatial orientation, kaja and kelod have the connotation of good and evil; gods and ancestors are believed to live on the mountain whereas demons live in the sea. Buildings such as temples and residential homes are spatially oriented by having the most sacred spaces closest to the mountain and the unclean places nearest to the sea.[29]
Most temples have an inner courtyard and an outer courtyard which are arranged with the inner courtyard furthest kaja. These spaces serve as performance venues since most Balinese rituals are accompanied by any combination of music, dance and drama. The performances that take place in the inner courtyard are classified as wali, the most sacred rituals which are offerings exclusively for the gods, while the outer courtyard is where bebali ceremonies are held, which are intended for gods and people. Lastly, performances meant solely for the entertainment of humans take place outside the walls of the temple and are called bali-balihan. This three-tiered system of classification was standardized in 1971 by a committee of Balinese officials and artists in order to better protect the sanctity of the oldest and most sacred Balinese rituals from being performed for a paying audience.[30]
Tourism, Bali’s chief industry, has provided the island with a foreign audience that is eager to pay for entertainment, thus creating new performance opportunities and more demand for performers. The impact of tourism is controversial since before it became integrated into the economy, the Balinese performing arts did not exist as a capitalist venture, and were not performed for entertainment outside of their respective ritual context. Since the 1930s sacred rituals such as the barong dance have been performed both in their original contexts, as well as exclusively for paying tourists. This has led to new versions of many of these performances which have developed according to the preferences of foreign audiences; some villages have a barong mask specifically for non-ritual performances as well as an older mask which is only used for sacred performances.[31]
Balinese society continues to revolve around each family's ancestral village, to which the cycle of life and religion is closely tied.[32] Coercive aspects of traditional society, such as customary law sanctions imposed by traditional authorities such as village councils (including "kasepekang", or shunning) have risen in importance as a consequence of the democratization and decentralization of Indonesia since 1998.[32]
Candi Borobudur Indonesia
Nama Borobudur
Banyak teori yang berusaha menjelaskan nama candi ini. Salah satunya menyatakan bahwa nama ini kemungkinan berasal dari kata Sambharabhudhara, yaitu artinya "gunung" (bhudara) di mana di lereng-lerengnya terletak teras-teras. Selain itu terdapat beberapa etimologi rakyat lainnya. Misalkan kata borobudur berasal dari ucapan "para Buddha" yang karena pergeseran bunyi menjadi borobudur. Penjelasan lain ialah bahwa nama ini berasal dari dua kata "bara" dan "beduhur". Kata bara konon berasal dari kata vihara, sementara ada pula penjelasan lain di mana bara berasal dari bahasa Sansekerta yang artinya kompleks candi atau biara dan beduhur artinya ialah "tinggi", atau mengingatkan dalam bahasa Bali yang berarti "di atas". Jadi maksudnya ialah sebuah biara atau asrama yang berada di tanah tinggi.Sejarawan J.G. de Casparis dalam disertasinya untuk mendapatkan gelar doktor pada 1950 berpendapat bahwa Borobudur adalah tempat pemujaan. Berdasarkan prasasti Karangtengah dan Kahulunan, Casparis memperkirakan pendiri Borobudur adalah raja Mataram dari wangsa Syailendra bernama Samaratungga, yang melakukan pembangunan sekitar tahun 824 M. Bangunan raksasa itu baru dapat diselesaikan pada masa putrinya, Ratu Pramudawardhani. Pembangunan Borobudur diperkirakan memakan waktu setengah abad. Dalam prasasti Karangtengah pula disebutkan mengenai penganugerahan tanah sima (tanah bebas pajak) oleh Çrī Kahulunan (Pramudawardhani) untuk memelihara Kamūlān yang disebut Bhūmisambhāra. [1] Istilah Kamūlān sendiri berasal dari kata mula yang berarti tempat asal muasal, bangunan suci untuk memuliakan leluhur, kemungkinan leluhur dari wangsa Sailendra. Casparis memperkirakan bahwa Bhūmi Sambhāra Bhudhāra dalam bahasa sansekerta yang berarti "Bukit himpunan kebajikan sepuluh tingkatan boddhisattwa", adalah nama asli Borobudur.[2]
[sunting] Struktur Borobudur
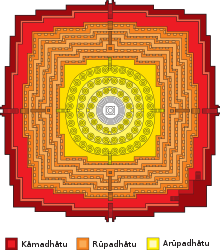
Denah Borobudur membentuk Mandala, lambang alam semesta dalam kosmologi Buddha.
Sepuluh pelataran yang dimiliki Borobudur menggambarkan secara jelas filsafat mazhab Mahayana. Bagaikan sebuah kitab, Borobudur menggambarkan sepuluh tingkatan Bodhisattva yang harus dilalui untuk mencapai kesempurnaan menjadi Buddha.
Bagian kaki Borobudur melambangkan Kamadhatu, yaitu dunia yang masih dikuasai oleh kama atau "nafsu rendah". Bagian ini sebagian besar tertutup oleh tumpukan batu yang diduga dibuat untuk memperkuat konstruksi candi. Pada bagian yang tertutup struktur tambahan ini terdapat 120 panel cerita Kammawibhangga. Sebagian kecil struktur tambahan itu disisihkan sehingga orang masih dapat melihat relief pada bagian ini.
Empat lantai dengan dinding berelief di atasnya oleh para ahli dinamakan Rupadhatu. Lantainya berbentuk persegi. Rupadhatu adalah dunia yang sudah dapat membebaskan diri dari nafsu, tetapi masih terikat oleh rupa dan bentuk. Tingkatan ini melambangkan alam antara yakni, antara alam bawah dan alam atas. Pada bagian Rupadhatu ini patung-patung Buddha terdapat pada ceruk-ceruk dinding di atas ballustrade atau selasar.
Mulai lantai kelima hingga ketujuh dindingnya tidak berelief. Tingkatan ini dinamakan Arupadhatu (yang berarti tidak berupa atau tidak berwujud). Denah lantai berbentuk lingkaran. Tingkatan ini melambangkan alam atas, di mana manusia sudah bebas dari segala keinginan dan ikatan bentuk dan rupa, namun belum mencapai nirwana. Patung-patung Buddha ditempatkan di dalam stupa yang ditutup berlubang-lubang seperti dalam kurungan. Dari luar patung-patung itu masih tampak samar-samar.
Tingkatan tertinggi yang menggambarkan ketiadaan wujud dilambangkan berupa stupa yang terbesar dan tertinggi. Stupa digambarkan polos tanpa lubang-lubang. Di dalam stupa terbesar ini pernah ditemukan patung Buddha yang tidak sempurna atau disebut juga unfinished Buddha, yang disalahsangkakan sebagai patung Adibuddha, padahal melalui penelitian lebih lanjut tidak pernah ada patung pada stupa utama, patung yang tidak selesai itu merupakan kesalahan pemahatnya pada zaman dahulu. menurut kepercayaan patung yang salah dalam proses pembuatannya memang tidak boleh dirusak. Penggalian arkeologi yang dilakukan di halaman candi ini menemukan banyak patung seperti ini.
Di masa lalu, beberapa patung Buddha bersama dengan 30 batu dengan relief, dua patung singa, beberapa batu berbentuk kala, tangga dan gerbang dikirimkan kepada Raja Thailand, Chulalongkorn yang mengunjungi Hindia Belanda (kini Indonesia) pada tahun 1896 sebagai hadiah dari pemerintah Hindia Belanda ketika itu.
Borobudur tidak memiliki ruang-ruang pemujaan seperti candi-candi lain. Yang ada ialah lorong-lorong panjang yang merupakan jalan sempit. Lorong-lorong dibatasi dinding mengelilingi candi tingkat demi tingkat. Di lorong-lorong inilah umat Buddha diperkirakan melakukan upacara berjalan kaki mengelilingi candi ke arah kanan. Bentuk bangunan tanpa ruangan dan struktur bertingkat-tingkat ini diduga merupakan perkembangan dari bentuk punden berundak, yang merupakan bentuk arsitektur asli dari masa prasejarah Indonesia.
Struktur Borobudur bila dilihat dari atas membentuk struktur Mandala.
Struktur Borobudur tidak memakai semen sama sekali, melainkan sistem interlock yaitu seperti balok-balok Lego yang bisa menempel tanpa lem.
[sunting] Relief
Di setiap tingkatan dipahat relief-relief pada dinding candi. Relief-relief ini dibaca sesuai arah jarum jam atau disebut mapradaksina dalam bahasa Jawa Kuna yang berasal dari bahasa Sansekerta daksina yang artinya ialah timur. Relief-relief ini bermacam-macam isi ceritanya, antara lain relief-relief cerita jātaka.Pembacaan cerita-cerita relief ini senantiasa dimulai, dan berakhir pada pintu gerbang sisi timur di setiap tingkatnya, mulainya di sebelah kiri dan berakhir di sebelah kanan pintu gerbang itu. Maka secara nyata bahwa sebelah timur adalah tangga naik yang sesungguhnya (utama) dan menuju puncak candi, artinya bahwa candi menghadap ke timur meskipun sisi-sisi lainnya serupa benar.
Adapun susunan dan pembagian relief cerita pada dinding dan pagar langkan candi adalah sebagai berikut.
| Bagan Relief | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tingkat | Posisi/letak | Cerita Relief | Jumlah Pigura |
| Kaki candi asli | - ----- | Karmawibhangga | 160 pigura |
| Tingkat I | - dinding | a. Lalitawistara | 120 pigura |
| ------- | - ----- | b. jataka/awadana | 120 pigura |
| ------- | - langkan | a. jataka/awadana | 372 pigura |
| ------- | - ----- | b. jataka/awadana | 128 pigura |
| Tingkat II | - dinding | Gandawyuha | 128 pigura |
| -------- | - langkan | jataka/awadana | 100 pigura |
| Tingkat III | - dinding | Gandawyuha | 88 pigura |
| -------- | - langkan | Gandawyuha | 88 pigura |
| Tingkat IV | - dinding | Gandawyuha | 84 pigura |
| -------- | - langkan | Gandawyuha | 72 pigura |
| -------- | Jumlah | -------- | 1460 pigura |
Karmawibhangga
Sesuai dengan makna simbolis pada kaki candi, relief yang menghiasi dinding batur yang terselubung tersebut menggambarkan hukum karma. Deretan relief tersebut bukan merupakan cerita seri (serial), tetapi pada setiap pigura menggambarkan suatu cerita yang mempunyai korelasi sebab akibat. Relief tersebut tidak saja memberi gambaran terhadap perbuatan tercela manusia disertai dengan hukuman yang akan diperolehnya, tetapi juga perbuatan baik manusia dan pahala. Secara keseluruhan merupakan penggambaran kehidupan manusia dalam lingkaran lahir - hidup - mati (samsara) yang tidak pernah berakhir, dan oleh agama Buddha rantai tersebutlah yang akan diakhiri untuk menuju kesempurnaan.
Lalitawistara
Merupakan penggambaran riwayat Sang Buddha dalam deretan relief-relief (tetapi bukan merupakan riwayat yang lengkap ) yang dimulai dari turunnya Sang Buddha dari sorga Tusita, dan berakhir dengan wejangan pertama di Taman Rusa dekat kota Banaras. Relief ini berderet dari tangga pada sisi sebelah selatan, setelah melampui deretan relief sebanyak 27 pigura yang dimulai dari tangga sisi timur. Ke-27 pigura tersebut menggambarkan kesibukan, baik di sorga maupun di dunia, sebagai persiapan untuk menyambut hadirnya penjelmaan terakhir Sang Bodhisattwa selaku calon Buddha. Relief tersebut menggambarkan lahirnya Sang Buddha di arcapada ini sebagai Pangeran Siddhartha, putra Raja Suddhodana dan Permaisuri Maya dari Negeri Kapilawastu. Relief tersebut berjumlah 120 pigura, yang berakhir dengan wejangan pertama, yang secara simbolis dinyatakan sebagai Pemutaran Roda Dharma, ajaran Sang Buddha di sebut dharma yang juga berarti "hukum", sedangkan dharma dilambangkan sebagai roda.
Jataka dan Awadana
Jataka adalah cerita tentang Sang Buddha sebelum dilahirkan sebagai Pangeran Siddharta. Isinya merupakan pokok penonjolan perbuatan baik, yang membedakan Sang Bodhisattwa dari makhluk lain manapun juga. Sesungguhnya, pengumpulan jasa/perbuatan baik merupakan tahapan persiapan dalam usaha menuju ketingkat ke-Buddha-an.
Sedangkan Awadana, pada dasarnya hampir sama dengan Jataka akan tetapi pelakunya bukan Sang Bodhisattwa, melainkan orang lain dan ceritanya dihimpun dalam kitab Diwyawadana yang berarti perbuatan mulia kedewaan, dan kitab Awadanasataka atau seratus cerita Awadana. Pada relief candi Borobudur jataka dan awadana, diperlakukan sama, artinya keduanya terdapat dalam deretan yang sama tanpa dibedakan. Himpunan yang paling terkenal dari kehidupan Sang Bodhisattwa adalah Jatakamala atau untaian cerita Jataka, karya penyair Aryasura dan jang hidup dalam abad ke-4 Masehi.
Gandawyuha
Merupakan deretan relief menghiasi dinding lorong ke-2,adalah cerita Sudhana yang berkelana tanpa mengenal lelah dalam usahanya mencari Pengetahuan Tertinggi tentang Kebenaran Sejati oleh Sudhana. Penggambarannya dalam 460 pigura didasarkan pada kitab suci Buddha Mahayana yang berjudul Gandawyuha, dan untuk bagian penutupnya berdasarkan cerita kitab lainnya yaitu Bhadracari.
[sunting] Arca Buddha
Selain wujud buddha dalam kosmologi buddhis yang terukir di dinding, di Borobudur terdapat banyak arca buddha duduk bersila dalam posisi lotus serta menampilkan mudra atau sikap tangan simbolis tertentu.Patung buddha dalam relung-relung di tingkat Rupadhatu, diatur berdasarkan barisan di sisi luar pagar langkan. Jumlahnya semakin berkurang pada sisi atasnya. Barisan pagar langkan pertama terdiri dari 104 relung, baris kedua 104 relung, baris ketiga 88 relung , baris keempat 72 relung, dan baris kelima 64 relung. Jumlah total terdapat 432 arca Buddha di tingkat Rupadhatu.[3] Pada bagian Arupadhatu (tiga pelataran melingkar), arca Buddha diletakkan di dalam stupa-stupa berterawang (berlubang). Pada pelataran melingkar pertama terdapat 32 stupa, pelataran kedua 24 stupa, dan pelataran ketiga terdapat 16 stupa, semuanya total 72 stupa.[3] Dari jumlah asli sebanyak 504 arca Buddha, lebih dari 300 telah rusak (kebanyakan tanpa kepala) dan 43 hilang (sejak penemuan monumen ini, kepala buddha sering dicuri sebagai barang koleksi, kebanyakan oleh museum luar negeri).[4]
Secara sepintas semua arca buddha ini terlihat serupa, akan tetapi terdapat perbedaan halus diantaranya, yaitu pada mudra atau posisi sikap tangan. Terdapat lima golongan mudra: Utara, Timur, Selatan, Barat, dan Tengah, kesemuanya berdasarkan lima arah utama kompas menurut ajaran Mahayana. Keempat pagar langkan memiliki empat mudra: Utara, Timur, Selatan, dan Barat, dimana masing-masing arca buddha yang menghadap arah tersebut menampilkan mudra yang khas. Arca Buddha pada pagar langkan kelima dan arca buddha di dalam 72 stupa berterawang di pelataran atas menampilkan mudra: Tengah atau Pusat. Masing-masing mudra melambangkan lima Dhyani Buddha; masing-masing dengan makna simbolisnya tersendiri.[5]
Mengikuti urutan Pradakshina yaitu gerakan mengelilingi searah jarum jam dimulai dari sisi Timur, maka mudra arca-arca buddha di Borobudur adalah:
Arca | Mudra | Melambangkan | Dhyani Buddha | Arah Mata Angin | Lokasi Arca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Bhumisparsa mudra | Memanggil bumi sebagai saksi | Aksobhya | Timur | Relung di pagar langkan 4 baris pertama Rupadhatu sisi timur |
 | Wara mudra | Kedermawanan | Ratnasambhawa | Selatan | Relung di pagar langkan 4 baris pertama Rupadhatu sisi selatan |
 | Dhyana mudra | Semadi atau meditasi | Amitabha | Barat | Relung di pagar langkan 4 baris pertama Rupadhatu sisi barat |
 | Abhaya mudra | Ketidakgentaran | Amoghasiddhi | Utara | Relung di pagar langkan 4 baris pertama Rupadhatu sisi utara |
 | Witarka mudra | Akal budi | Wairocana | Tengah | Relung di pagar langkan baris kelima (teratas) Rupadhatu semua sisi |
 | Dharmachakra mudra | Pemutaran roda dharma | Wairocana | Tengah | Di dalam 72 stupa di 3 teras melingkar Arupadhatu |
[sunting] Tahapan pembangunan Borobudur
- Tahap pertama
- Tahap kedua
- Tahap ketiga
- Tahap keempat
[sunting] Ikhtisar waktu proses pemugaran Candi Borobudur
- 1814 - Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles, Gubernur Jenderal Britania Raya di Jawa, mendengar adanya penemuan benda purbakala di desa Borobudur. Raffles memerintahkan H.C. Cornelius untuk menyelidiki lokasi penemuan, berupa bukit yang dipenuhi semak belukar.
- 1873 - monografi pertama tentang candi diterbitkan.
- 1900 - pemerintahan Hindia Belanda menetapkan sebuah panitia pemugaran dan perawatan candi Borobudur.
- 1907 - Theodoor van Erp memimpin pemugaran hingga tahun 1911.
- 1926 - Borobudur dipugar kembali, tapi terhenti pada tahun 1940 akibat krisis malaise dan Perang Dunia II.
- 1956 - Pemerintah Indonesia meminta bantuan UNESCO. Prof. Dr. C. Coremans datang ke Indonesia dari Belgia untuk meneliti sebab-sebab kerusakan Borobudur.
- 1963 - Pemerintah Indonesia mengeluarkan surat keputusan untuk memugar Borobudur, tapi berantakan setelah terjadi peristiwa G-30-S.
- 1968 - Pada konferensi-15 di Perancis, UNESCO setuju untuk memberi bantuan untuk menyelamatkan Borobudur.
- 1972 - International Consultative Committee dibentuk dengan melibatkan berbagai negara dan Roosseno sebagai ketuanya. Komite yang disponsori UNESCO menyediakan 5 juta dolar Amerika Serikat dari biaya pemugaran 7.750 juta dolar Amerika Serikat. Sisanya ditanggung Indonesia.
- 10 Agustus 1973 - Presiden Soeharto meresmikan dimulainya pemugaran Borobudur; pemugaran selesai pada tahun 1984
- 21 Januari 1985 - terjadi serangan bom yang merusakkan beberapa stupa pada Candi Borobudur yang kemudian segera diperbaiki kembali. Serangan dilakukan oleh kelompok Islam ekstremis yang dipimpin oleh Husein Ali Al Habsyi.
- 1991 - Borobudur ditetapkan sebagai Warisan Dunia UNESCO.
Langganan:
Postingan (Atom)





















